BENEFITS OF I2U2 TO INDIA (5:10 PM):
- This is the first time India is engaging in West Asia at a plurilateral level( generally 4-6 member countries).
- India earlier engaged only in a bilateral manner in West Asia.
- India stayed away from West Asia politics to ensure energy safety and the safety of its diaspora.
- Expansion of scope for the India-USA cooperation beyond the Indo-Pacific region.
- This is crucial because India has traditionally opposed American intervention in the region.
- India has generally been apprehensive of the West's role in West Asia.
- Though the body claims itself as a geo-economic grouping, its geostrategic logic to counter China cannot be ignored.
Challenges with I2U2:
- The rest three members are critical of Iran, and they might adopt an anti-Iran agenda through the platform.
- This could impact India's long-standing relations with Iran.
- Presently, I2U2 would enable India to build mutually beneficial economic partnerships with the other three countries without any adverse impact on India's strategic autonomy.
INDIA SAUDI-ARABIA RELATIONS (5:30 PM):
Importance of Saudi Arabia:
I. Energy Security:
- Saudi Arabia is the second largest supplier of crude oil(18% to India; Iraq is the largest supplier.
- Saudi Arabia also supplies 30% of Indian LPG imports.
II. Remittances & Diaspora:
- 2.4 million Indians live in Saudi Arabia which is 7% of the kingdom's population.
- India is the largest recipient of remittances from the kingdom.
III. Trade & Investments:
- In the financial year 2022-2023, the bilateral trade stood at $52 billion which is 23% higher on a year-to-year basis.
- Saudi Arabia is the fourth largest trading partner of India and India is its second largest trade trade partner.
- During the September 2023 state visit by the Crown Prince & Prime Minister Mohammad Bin Salman( MBS), two points were discussed:
- I. The two countries discussed the possibilities of trading in local currencies.
- We signed a similar agreement with UAE and we are pushing for de-dollarization in BRICS.
- II. Explored the opportunity for cooperation in payment systems, including the acceptance of Rupay Cards in Saudi Arabia.
- Currency usability will largely benefit the Indian diaspora and Haj pilgrims.
- During MBS's visit in 2019, the kingdom promised to invest $ 100 billion in India.
- A trilateral project to establish the world's largest green field refinery to be built on the Maharashtra coast between ARAMCO, ADNOC, and Indian PSUs.
- Saudi will invest $ 50 billion of the $100 billion in the project -the Raigad refinery cum Petroleum Complex.
Socio-Cultural Cooperation:
- Saudi Arabia is home to two of Islam's holiest sites- Mecca & Medina, so it is the leader of the Islamic world.
- Indis is home to the second largest Muslim population in the world after Indonesia.
- Hence, the socio-cultural importance arises.
Strategic Importance:
- The two countries have a strategic partnership, cooperate in counter-terrorism, and have a common foreign policy agenda in Afghanistan.
- Both countries have repeated the need for inclusive government in Afghanistan which represents the " All Spectrum of the Afghan people".
- The two countries have also identified defense, energy security, space, and semiconductors as focused areas of cooperation.
- Saudi has assured India that it would remain a "Reliable partner" and exporter of crude oil supplies.
- Saudi recently joined the BRICS which hopes to restructure global governance models.
India- Middle East- Europe Economic Corridor(IMEC) Rail & Port connectivity corridor:
- Member countries are the USA, Saudi Arabia, UAE, India and the EU.
- IMEC is being perceived as a counter to China's BRI.
STATEMENTS BY PM MODI (6:00 PM):
- He described Saudi Arabia as " one of the most strategic partners to India".
- As two of the world's fastest-growing economies, our partnership is important for the stability of the entire region- global economic stability.
Evolution of bilateral ties:
- The two countries have centuries-old economic and socio-cultural ties.
Modern Cooperation:
- 2006-:
- Saudi King visited India.
- The Delhi Declaration was signed.
- 2010:
- Indian PM paid a visit to Saudi and the Riyadh Declaration was signed.
- We entered into a Strategic Partnership Agreement.
- The above two declarations are the stepping stones of modern India-Saudi relations.
- 2016:
- PM Modi's visit to Saudi was referred to as a turning point in our relations by our Ministry of External Affairs.
- He was also awarded the highest civilian honor- King Abdulaziz Sash.
- 2019:
- MBS was on a tri-nation visit to India, Pakistan & China.
- India-Pakistan relations were at their lowest point in the backdrop of the Pulwama attack.
- The momentum of the relations was taken forward and he announced $100 billion in investments in India.
- The India-Saudi Arabia Strategic Partnership Council(SPC) was formed under Vision 2030 of the kingdom.
- The Vision 2030 has been put forth by MBS with the primary aim of economic diversification.
-
Some reasons for the Vision 2030:
- Saudi's apprehension after the Arab Spring.
- Arab Spring refers to a series of anti-government protests that started in Tunisia in 2010 and spread to many other Arab nations.
- The main reasons were human rights violations, corruption, poverty, unemployment, etc.
- Regimes were changed in Tunisia. Egypt & Yemen
- Much of the Saudi economy is dependent on fossil fuels which are finite.
- The global interest in renewable energy is pushing Saudi to diversify its economic portfolio.
- Under the vision, Saudi has envisaged forming SPC with 8 countries including India.
- India Saudi SPC comprises two main pillars namely:
- I. Political, Security, Social & Cultural Committee.
- II. The Committee on Economy & Investment.
- In September 2023, MBS visited India to participate in the G 20 Summit and then stayed back for a state visit.
- Recently, PM Modi and MBS co-chaired the first meeting of the India-Saudi SPC.
- The ties between the two countries are no longer limited to bilateral cooperation.
- The cooperation is also expanding to multilateral platforms like:
- Saudi Arabia has become a member of the BRICS and IMEC corridor.
Major Breaks in India-Saudi Arabia relations:
- From bilateral to plurilateral.
- Cooperation of Afghanistan- both have called for a more representative govt.
- Cooperation on counter-terrorism.
-
- Saudi Arabia supported Pakistan in fostering the Taliban.
- Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Pakistan were the only three nations that recognized the Talian government in 1996.
- Exploring local currency settlement of bilateral trade
- The USA was the regional hegemon and close ties between Saudi and the USA, so much so that Saudi Arabia has been under the security umbrella of the USA.
- In 1945, the USA guaranteed American security for the Kingdom in return for crude oil.
- The agreement has not ended officially, but we see considerable receding of the American umbrella.
- MBS denied American requests to increase oil production during the Russia- Ukraine war.
INDIA-GCC COOPERATION (6:35 PM):
- In 2022, India and GCC signed an MOU to institutionalize an annual dialogue.
- India and GCC are to expedite negotiations for an FTA.
- GCC is India's largest trading partner block with over $150 billion in trade.
- GCC countries contribute to almost 30% of Indian oil imports and 70% of gas imports.
- GCC is a major source of FDI into India- over $18 million in investments.
Bilateral Issues between India & Saudi Arabia:
I. Rising islamophobia in India:
- The annual prayer meeting of the Tablighi Jamaat was termed a Super Spreader during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- That too when we saw other religious festivals and
- Derogatory remarks against Prophet Mohammad in India which UAE and Organization of Islamic Cooperation(OIC) criticized publicly.
II. Saudi's ideological support for Islamic terrorism:
- The Taliban was trained in the Wahhabi ideology of the kingdom.
III. Saudi-Pakistan relations:
- They are historical allies tied by a common theological bridge(Sunni Islam).
- saudi has traditionally supported the Pakistani view on Kashmir.
-
- However, in the context of the abrogation of Article 370, Saudi opposed Islamabad's aim to use the platform of OIC to internationalize the issue.
- Saudi in fact termed it an internal matter of India.
IV. Saudi's aggressive foreign policy in West Asia:
- It can be seen through steps like imposing an economic blockade on Qatar and engaging in a proxy war with Iran in Yemen.
- It damages regional stability which is against Indian interests.
V. China in West Asia:
- China is a leading buyer of Saudi oil.
VI. Indian diaspora:
- Indians there are subjected to restrictive visas, stringent labor laws, violation of human rights, absence of minimum wage provisions, etc. causing exploitation of Indian workers.
- However, these concerns are being increasingly addressed by the kingdom.
INDIA UAE RELATIONS (7:00 PM):
- 2015:
- A strategic partnership agreement was signed between India and UAE.
- This was a major event as UAE has traditionally supported the Taliban in 1996 and Pakistan over Kashmir.
- 2022:
- We entered into a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA).
- This was the first FTA signed by the Modi government in 9 years.
- It is the first CEPA ever in the UAE, while India has CEPAs with Japan, South Korea, etc.
- CEPA entails trade in goods and services.
- So it is comprehensive in nature against many of the Early Harvest Agreements(EHA) or interim agreements concluded by India.
- EHA is an interim agreement till both sides conclude in a comprehensive manner.
- It was negotiated through a fast-track three-month negotiations between the two countries.
- We have been negotiating such an agreement with the EU since 2007, the UK after Brexit 2020, the USA under Trump, etc.
- It caters to India's concerns such as stringent rules of origin clause which would prevent goods from other countries from entering into the Indian market using the route of UAE.
-
Why India is so serious about Strict Rules of Origin?
- The Indian manufacturing sector is still not fully developed.
- If India has an FTA with a nation with strong manufacturing( China), the Indian market will get flooded with Chinese goods and Indian firms will face high losses.
- It is possible that China will sign an FTA with the UAE, and first Chinese goods will enter into UAE and then Chinese goods will enter into India under the India-UAE CEPA.
- Even this condition will be bad for Indian manufacturers.
- This situation will be prevented if the India-UAE CEPA has strict rules of origin.
- CEPA also has an Automatic Trigger Safeguard Mechanism (ATSM) to protect our nascent manufacturing sector.
- It excludes provisions such as the investor-state dispute settlement mechanism, with which India has had problems.
- In July 2023, PM Modi visited the UAE, and two MOUs were signed:
I. Local Currency Settlement System(LCSS) to promote the use of Rupee and Dirham bilaterally.
- It would enable payments in the respective domestic currencies which would in turn help in the development of the Rupee-Dirham foreign exchange market.
- It would optimize transaction costs and settlement time for transactions including remittances between India and UAE.
- It would also avoid exchange rate risks- when a third currency is used for bilateral trade(US dollar).
- It would facilitate a more competitive price discovery and hence promote trade.
II. It links Indian UPI with the Instant Payment Platform (IPP), the UAE's counterpart.
- It would help safe and effective cross-border fund transfers.
- Strategic cooperation in fields of counter-terrorism, extradition treaty.
- India acquired the Duqm port of Oman for dual-use- civilian and naval.
-
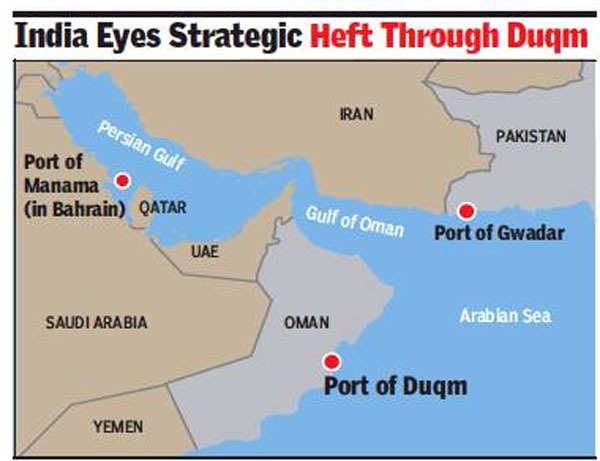
-

India UAE Economic relations:
- UAE is India's third-largest trading partner and second-largest export destination in financial year 2022-2023.
- India is the UAE's third-largest trading partner.
- UAE is among the top five investors (source of FDI in India).
|
INDIA-IRAN RELATIONS (7:35 PM):
- Importance of Iran for India:
I. Connectivity:
- We have envisaged "Prosperity Through Greater Connectivity".
- Iran is essential to develop connectivity with its extended western neighborhood- Afghanistan and Central Asia.
- Chabahar port and INSTC are important connectivity projects.
-
II. Geopolitical/ Geostrategic importance:
- To counter Chinese String of Pearls.
- To cooperate with respect to Afghanistan.
- It was Iran who led the Regional Security Dialogue at the NSA level over Afghanistan.
- Both want inclusive government and peace in Afghanistan.
III. For counter-terrorism:
- Iran is an important partner against groups like ISIS, Al Qaeda, etc.
- It is an important geo-political actor responsible for the overall stability of West Asia.
-
Iran's Proxies/Supported Groups Country Houthi Rebels Yemen Hezbollah Lebanon Hamas Palestine - Iran has a Quds force for extra-territorial wars.
- The USA needed the cooperation with Quds against ISIS.
Energy Security:
- Prior to the American Sanctions in 2003, Iran was among the largest crude suppliers to India.
- It has the world's second-largest reserves of natural gas.
Evolution of India-Iran relations:
Phase I- 1950-1979:
- A treaty of friendship was signed with Iran in 1950.
- Historically, we have shared close civilizational ties.
- We used to share land borders before partition.
- The relations were overall tepid during Cold War politics.
- Monarchial Iran was in an American camp while India was a leader of the NAM
Phase II- 1979-1990:
- After the Islamic Revolution in 1979, the monarchy was abolished and Iran became a theocratic republic.
- Consequently, Iran came out of the American camp.
- It was expected that India-Iran relations would improve, but the opposite happened.
- Since it became a theocratic state, it wanted to assume the leadership of the Islamic world and therefore became a more ardent supporter of Pakistan over Kashmir.
- India and Iran were hence pulled apart.
Phase III- 1990-2003:
- After the Soviet withdrawal from Afghanistan in 1989, there was civil war and instability in Afghanistan.
- Afghanistan became the ground for sponsoring cross-border terrorism in India.
- Since Afghanistan shared borders with Iran, Iran was careful regarding instability.
- India and Iran grew closer with the Taliban taking over Kabul.
- Both had common objectives in Afghanistan.
- This phase saw improvement in bilateral relationships.
- 2001:
- The then-Indian PM visited Iran for the Tehran Declaration.
- 2003:
- The Iranian President was invited as a chief guest to Indian Republic Day celebrations.
- The Iran-Pakistan-India(IPI) was envisaged
Phase IV- After 2003:
- Iran's secret nuclear weapon program came to light and since then the USA began to interpose India-Iran relations.
The topic for the next class is the continuation of India-Iran relations